If you are hired to develop a production level python application then you have to adhere to certain code standards , often developers write their codes which look easy and understandable to them but actually it’s not. So to maintain code quality we can use different code quality management tools.
If you worked with PyCharm, you will note that the inspections plugin that performs static analysis on your code is very effective in identifying errors in PEP-8. Yet in some cases this fails and can be replaced with pylint. This tutorial will direct you through the setting up of pylint in PyCharm step by step in Windows.
What is Static code analysis?
The main task of static code analysis tool is to evaluate compiled computer code or source code analysis, so that bugs can be quickly found without running the program.
- Provides insight into code without executing it
- Can automate code quality maintenance in the early stages
- Can automate early on discovering security problems
- Rapidly executes in contrast with dynamic analysis
Note: You already using it (if you use any IDE that already has static analyzers, Pycharm uses pep8 for example).
What Static code analysis does for you?
- Code styling analysis
- Duplicate code detection
- Complexity analysis
- Comment styling analysis
- Security linting
- Unused code detection
- Error detection
- UML diagram creation
1. Locate your pylint installation
If you don’t have pylint installed then try the command abover after installing pylint via pip.
$ pip install pylint
If it’s installed then below commands will work for you. For windows:
$ where pylint .\Python\Python36\Scripts\pylint.exe
2. Go to External tools in PyCharm
You can find the External Tools options from the
- File -> Settings
- Typing External Tools in the search bar
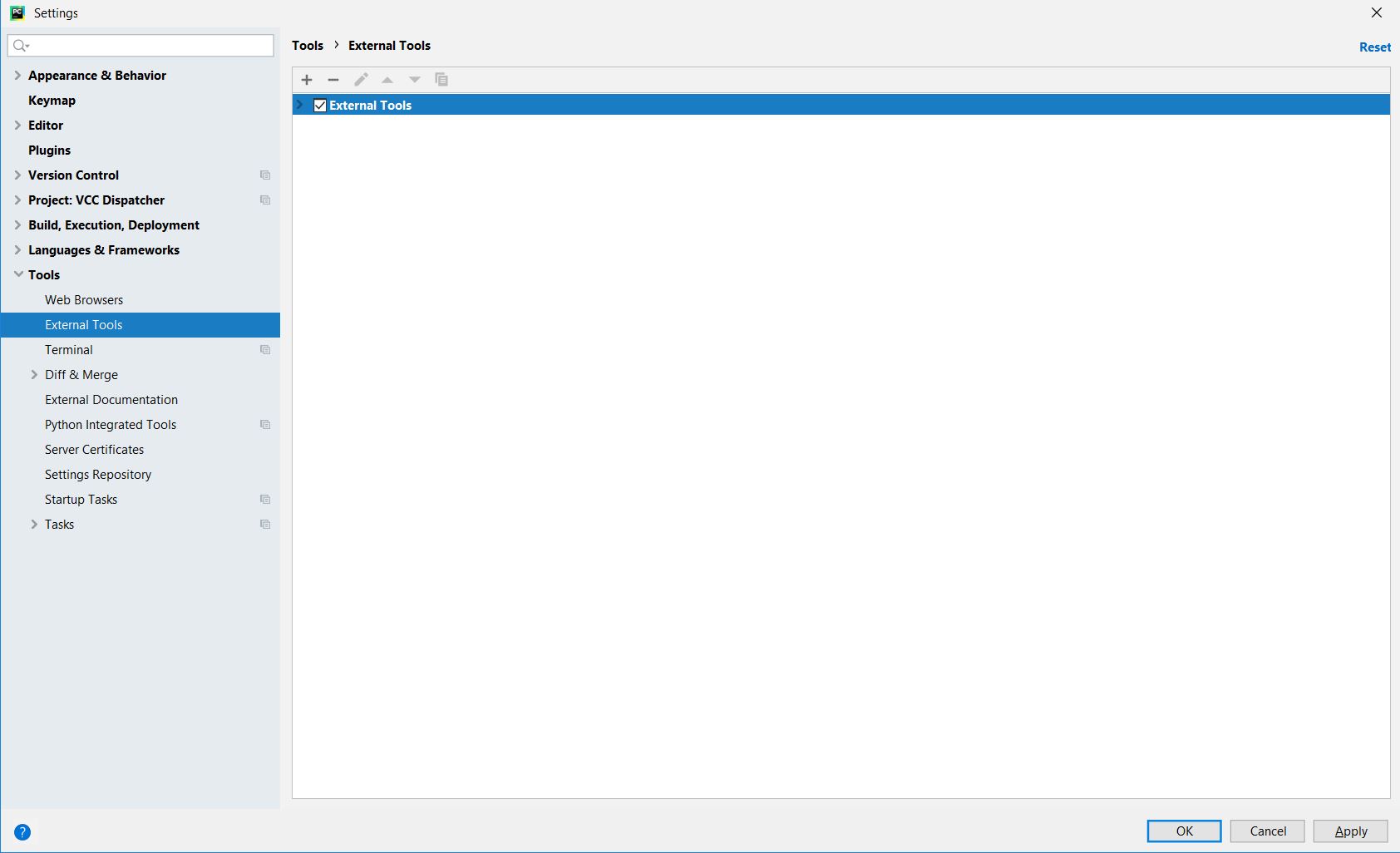
You can read more about External Tools here.
3. Add Pylint as an External Tool
Tap on the’ +’ button in the* External Tools* window and customize using the details below.
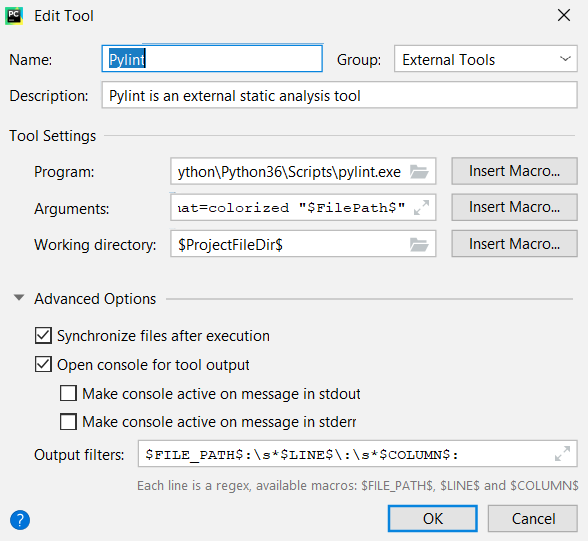
- Program: Use the path found in Step 1.
- Arguments: “–msg-template=’{abspath}:{line:5d}:{column}: {msg_id}: {msg} ({symbol})’” –output-format=colorized “$FilePath$”
- Working directory: $ProjectFileDir$
- Output filters: $FILE_PATH$:\s$LINE$:\s$COLUMN$:
4. Run Pylint on entire project or a single file
To run on a single file:
Run pylint from External Tools via Tools -> External Tools -> pylint dropdown.
To run on the entire project:
- Right click on the root directory.
- Run
pylintfrom External Tools via External Tools -> pylint* dropdown.
5. Check your Pylint score on PyCharm console
After your run from Step 4, you can view your pylint score in your PyCharm console.
Pylint prefixes each of the problem areas with an R, C, W, E, or F, meaning:
- [R]efactor for “good practice” metric violation
- [C]onvention for coding standard violation
- [W]arning for stylistic problems, or minor programming issues
- [E]rror for important programming issues (i.e. most probably a bug)
- [F]atal for errors which prevented further processing
Regarding the coding style, Pylint follows the PEP8 style guide.
6. Configure Pylint to as per your requirement
You can configure Pylint with a ~/.pylintrc file-this allows you to ignore warnings you don’t care about, amongst other things.
- At first generate the global configuration file in your project directory by below command:
$ pylint --generate-rcfile > .pylintrc
- Once it is generated you may put it in:
- /etc/pylintrc for default global configuration
- ~/.pylintrc for default user configuration
-
/pylintrc for default project configuration (used when you'll run pylint ) - wherever you want, then use pylint –rcfile= Given path
Do remember when generating the rc file, you can add option to the command line before the —generate-rcfile to be included in the generated file.
I don’t recommend a system-wide or user-wide rc file against this. Using it per project is almost always fine.
Example of a configuration change:
- To disable other warnings, use Message Control to turn them off individually:
[MESSAGES CONTROL] # C0111: Missing docstring # R0904: Too many public methods disable=C0111,R0904
Keep this config file in your project root folder and run Pylint.
- Now Pylint would not check for these two problems.
Congratulations!! Now you are ready to write some powerful applications!!
Reference:





Leave a comment